Business
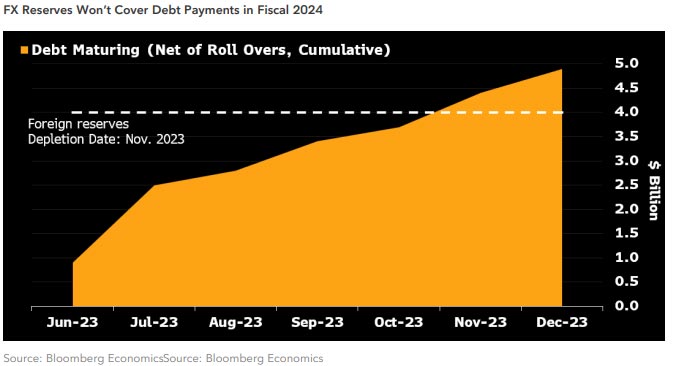
Pakistan’s default odds rise as IMF sours on bailout: Bloomberg
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days ago52 districts in Pakistan have 52 cases of the polio virus.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoFederal Cabinet once again postpones decision on PTI suspension and Article 6 action against Imran and Alvi
-

 Entertainment3 days ago
Entertainment3 days agoA glimpse of Sania Mirza’s relaxed moments
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoElection Amendment Act Case Heard by IHC; Response Requested From Law Ministry, ECP Within Ten Days
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoThe 10th Executive Committee Meeting of SIFC examines the role of provinces in bringing in foreign investment.
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoCabinet will probably decide today whether to ban PTI: Fawad ChaudhryCabinet will probably decide today whether to ban PTI: Fawad Chaudhry
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoMubarak Sani Case: Punjab Government’s Review Petition Accepted by the SC
-

 Latest News3 days ago
Latest News3 days agoPakistan has advanced to the Women’s Asia Cup 2024 semifinals.